What is Shoring | Shoring Types and Uses in Construction
Shoring is the process of giving temporary support to a building or structure with shores on verge of collapse.
Application of Shoring
Shoring in Construction serves the following purpose:
- Provides support to walls that might become unstable because of subsidence, bulging, or leaning.
- Prevents failure of sound walls caused by the removal of underlying support, such as where a basement is being constructed near a sound wall.
- Adds support to an adjacent building or structure during demolition works.
- Gives support to the upper part of a wall during the formation of a large opening in the lower section of the wall.
- Contribute support to a floor or roof to enable a support wall to be removed and replaced by a beam.
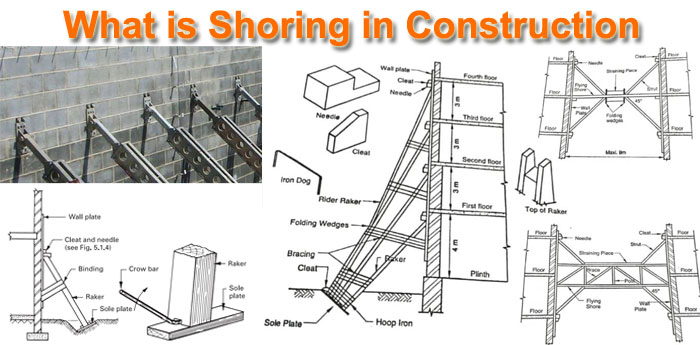
Types of Shoring in Construction:
Shoring systems have their own function to perform. Following are the types of shoring systems:
1. Dead Shoring
This is the type of shoring that helps in providing support to the dead loads acting vertically downwards. This type of sharing usually has a vertical prop or shore leg having a head plate, soleplate, and adjustment needed to tighten and ease the shore.
The arrangement is made in a way where two shore legs are linked over their heads by a horizontal beam/needle, which transfers the load to the shore legs and further down to a solid bearing surface.
It is necessary to remove paving and cut holes in suspended timber floors to reach a suitable bearing surface; a third horizontal member called a transom would be necessary as it is not possible to manipulate a shore leg through two stories.
The sequence of operations necessary for dead shoring arrangement is:
- A thorough site investigation should be carried out to determine:
- Number of shores required by ascertaining possible loadings and placements of the window.
- Bearing capacity of floors and soil.
- Underground services location that may have to be avoided.
- Fixation of ceiling struts between the suitable head and sole plates is done to relieve the floorwall and roof loads.
- The struts should be positioned as close to the wall as possible.
- All window openings are strut within the shore area to prevent movement or distortion of the opening.
- Positioning timber plates against the external reveals.
- Placing strut between external reveals.
- Cutting holes through the wall slightly larger in size than the needles.
- For the shore legs, cutting holes through ceilings and floors.
- Position and level sleepers on a firm base, paving removal if necessary.
- Erect, wedge, and secure shoring arrangements.
The shoring needs to be left in position upon completion of the builder’s work, for at least seven days before easing the supports, to ensure the new work has gained sufficient strength to be self-supporting.
2. Raking Shoring
This type of shoring arrangement helps in transferring the loads over the floor and wall to the ground by means of sloping struts also called rakers. The rakers need to be correctly placed so that they are capable of receiving maximum loads from floors and walls.
The centreline of the raker should intersect with that of the floor or wall bearing.
For each floor, a rake is required which should be at an angle ranging between 40° and 70° horizontally. The number of rakes that can be used is generally limited to three.
By this method, a four-story building can be shored, if an extra member (a rider), is added.
The sequence for erecting raking shoring is:
- Site investigation needs to be carried out as described for dead shoring.
- Mortises and housings are cut and marked out on a wall plate.
- Holes for needles are set out and cut in an external wall.
- Firm bearing subsoil is dig and grillage platform and sole-plate laid.
- Rakers are cut and erected, commencing with the bottom shore.
- Cleats, distance blocks, binding are fixed.
- If necessary, cross-bracing id done over the backs of the shores.
3. Flying Shoring
Flying shores perform the same functions as raking shores. It provides a clear working space under the shoring, which seems to be an advantage. They can be used between any parallel walls surfaces.