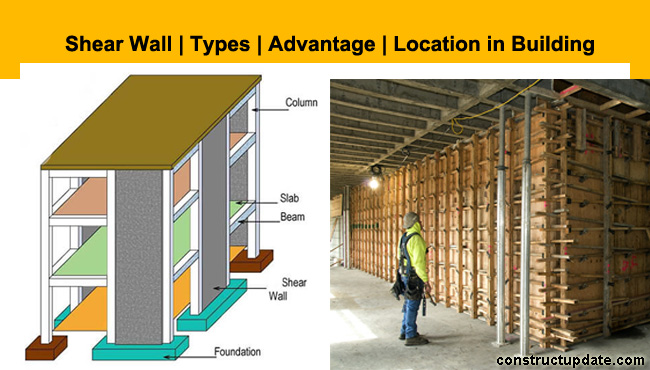
Shear Walls and its Types | Reinforced Concrete Shear Wall Location, Advantages
What is Shear Wall?
An element used to resist lateral forces like wind, seismic forces acting on the structure of a building is known as the ‘Shear Wall’.
Mainly used in tall buildings, they are vertical cantilever beams supported at the ground, which carry vertical loads with columns together.
Shear walls, in past two decades has become an important part of high rise building.
They are provided in building plans for reducing the lateral displacements under earthquake loads.
Purpose to use Shear Walls in a building:
- Resists the lateral loads of winds and earthquakes.
- Resists gravity or vertical loads of self-weight.
- Resists other living/moving loads.
- Resists shear.
- Uplift forces on a building.
- Enhances strength and stability of a building structure.
- Provides stiffness to the structure adequately.
What is Shear Wall-Location in a Building:
Arrangements of Shear Walls are basically of two types-
- Shear Walls are Located at the edges of the building (plane or flanged shaped).
2. Shear Walls are Located inside the building (in shape of core walls or channel sections).
In high-rise buildings, these walls are placed at the center of the building in the form of a core wall system that accommodates lift.
Shear Wall- Forces Acting on Shear Wall :
Shear Walls resists mostly two types of forces-
Shear Force: Produced due to ground movement and lateral forces such as waves, winds. They act between the top and bottom wall connections throughout the wall height.
Uplift Force: Produced due to forces acting horizontally on the top of the wall. These forces lift up one end of the wall by pushing down the other end. They create great effects on tall-short walls and fewer effects on long-low walls. To provide necessary uplift resistivity, these forces require to hold down devices sometimes.
Classification of Shear Walls:
Shear Walls are classified into following categories-
- Simple rectangular/Flanged walls.
- Coupled Shear Walls.
- Rigid Frame Shear Walls.
- Framed Walls with in-filled frames.
- Column supported Shear Walls.
- Core type Shear Walls.
Types of Shear Walls:
1. RC Shear Walls:
- Consisting RC slabs and Reinforced concrete walls.
- Thickness of walls varies from 140mm–150mm
- RC Shear Walls continue throughout the height of the building.
- On streets or for parking space in basement, discontinuous walls are constructed.
2. Steel Plate Shear Walls:
- Consisting boundary columns, horizontal floor beams and steel plates.
- Steel plate walls and boundary columns acts as vertical plate girder;
- Column acts as flanges and steel plates acts as the web.
- Used frequently in high seismic areas.
- Expensive as compared to the other types.
3. Plywood Shear Walls:
- Consisting of plywood, base connections, and chords.
- Shear forces are transferred by plywood;
- tension and compressions get resisted by the chords,
- shear gets transferred to the foundation by the base connection.
4. RC Hollow Concrete Block Masonry Wall:
- Constructed by providing steel reinforcement in both horizontal and vertical directions of masonry blocks.
- These walls counter forces and seismic loads, withstanding earthquakes.
- This concept is also known as the diaphragm concept gives 3-D stability to the building.
5. Mid-ply Shear Wall:
- A new concept where a ply of sheathing material is placed t the wall center.
- Centre of the wall is between a series of stud pairs and plates.
- These plates are oriented in 90 degrees rotated position.
- Steel rods are used at each end of mid-ply walls.
- Steel rods are used to prevent brittle failure at the end stud due to high tension forces.
- These walls can withstand earthquake, dynamic loads compared to three times standard walls
Advantages of Shear Wall:
- Reduces lateral sway of the building.
- Provides strength, stability, and stiffness to the building structure.
- Construction and implementations are easy at the site.
- Walls being thinner are thus light-weight.
- Helps minimize the damage to structural and non-structural elements due to earthquakes and other forces.
- Lesser cost, faster construction, time-saving, long-lasting.