Grillage Foundation Types | Grillage Foundation Design | Grillage Foundation Advantages, Disadvantages
What is a Grillage Foundation?
A grillage foundation is made composed of one, two, or more layers of beams (usually steel) overlaid on a concrete layer to distribute the load over a large surface.
At the base of the columns, it’s used. These layers are concrete-wrapped and at right angles to one another. This sort of foundation is typically utilized for heavy-duty pillars and column scaffolds.
Although the foundation and grid appear to be the same, they are not. The grid disperses heavy loads over wide areas, similar to how the foundation transmits load from the structure to the ground.
Types of Grillage Foundation
- Steel Grillage Foundation
- Timber Grillage Foundation
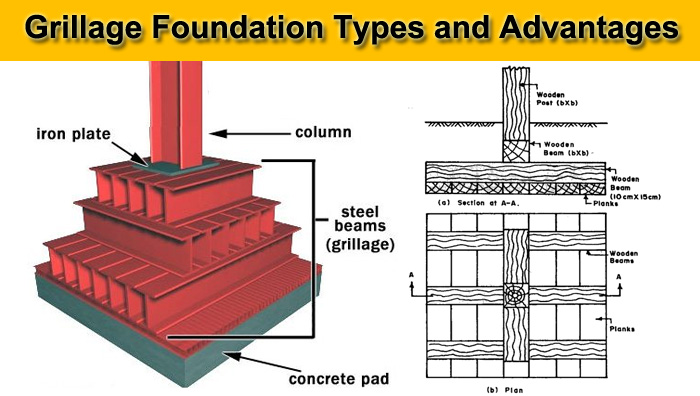
1. Steel Grillage Foundation
Steel grillage foundations are made up of single or double levels of steel joints or beams. Because it is constructed up of steel beams, structurally known as rolled steel joists, its name defines its function and structure.
On the outside sides of the exterior beams, as well as above the upper flanges of the top tier, a minimum cover of 10 cm is maintained.
Concrete should be poured to a depth of at least 15 cm. After levelling the base and pouring the concrete, we should inspect for correct compaction and the formation of an impermeable layer with a thickness of at least 15 cm.
It protects steel joists from corrosion caused by groundwater. Then, using pipe separators, we place the first layer of beams over the concrete bed at a distance of 100mm to 300mm.
After that, we pour concrete between and around the first tier’s beams. With the help of the separator, we then install the second tier of the beam at a right angle to the first levels.
Then there’s the concrete pouring between and around the steel beams. With the help of a base plate, side angles, and a gusset plate, we link the steel stanchions to the higher tier. To make the junction rigid, these connecting pieces are also embedded in the concrete.
2. Timber Grillage Foundation
For masonry walls strongly loaded with Timber columns, a timber-type base is supplied.
This foundation is particularly beneficial in flooded locations, where the soil’s bearing capacity is low and the load on the soil is restricted to 50-60 KN/M2.
Steel beams are replaced with timber planks and beams. Between the Timber joints, there is no concrete.
However, the steel grid’s lower concrete is replaced with a Timber platform made of Timber boards.
The base’s excavation is level. The bottom layer is made up of 20 to 30 cm wide and 5 to 7.5 cm thick timber planks that are laid side by side with no space between them.
Grillage Foundation Design
Calculating the loads and moments from the superstructure is necessary for grillage foundation design.
We must determine the required foundation area for a sufficient permissible ground bearing pressure of the condition based on this. We’ll determine the number and size of each grillage layer by dividing this space.
The layer must then be designed in such a way that it cantilevers from the one above it. It will calculate the size of the beams needed to withstand the bending moments and shear forces.
The grillage cannot be encased in concrete and the order, since this would demoralize the beam’s and concrete’s composite activity. Construction and loading methods must be compatible with one another.
Grillage Foundation Advantages
- Installation takes less time and requires fewer resources.
- Because it is not sprayed to frozen earth, it reduces the transfer of heat from the house through the foundation.
- It lowers the house’s vibration level (it is very real if the house is built close to highways).
- Grillage Beam installation takes less time and uses fewer materials.
- Significant constructions, such as column piers and scaffolds, can be supported by this form of foundation.
- It has the ability to distribute the load over a broader region.
Disadvantages of Grillage Foundation
- It necessitates the construction of piles of suitable depth.
- It is necessary to fill and heat the space beneath the grid.
- It is necessary to excavate a greater area, which raises the excavation cost.
- A greater lifting force has an impact on it.
- In this type of foundation, column alignment may shift somewhat.




