Difference between Tension and Compression | Tension Vs Compression
For the study, initially we need to know about ‘Force’.
Force:
When an object interacts with another object, it results in a push or pull acting on each object. This interaction between two objects resulting in push or pull of the objects is defined as ‘Force’. Whenever there is an interaction between two objects, there is force acting on both the objects with mass that results in change in velocity(the speed with which an object moves in a particular direction).
A particular body or object can have a complete change of state of rest or motion due to Force. Force exist only when a minimum of two objects interacts.
The standard metric unit called Newton abbreviated as ‘N’ is used to measure Force. One Newton is the amount of force needed to give acceleration to a kilogram of mass at the rate of a metre per second squared in the direction of the force applied.
Forces are of two types-
- Contact Force.
- Non-Contact Force.
Two principal forces involved in any structure or building are – Tension and Compression.
Each material has its own ability to handle tension and compression to certain point. Some material can bear tension easily, while some can withstand compression. Some has the ability to handle and withstand both tension and compression easily.
For example, if we pull a rope, it can it can bear a certain amount of tension whereas, pushing it can make it resist compression (by bending).
A note on Tension:
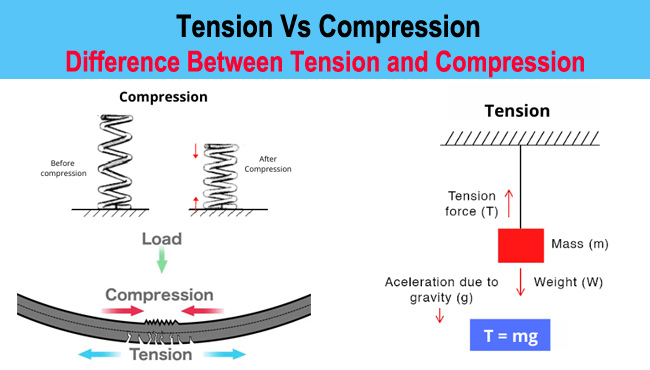
Tension means ‘Stretch’. Some forces act away from each other referring to ‘Tension Force’. Therefore we can say, a force that pulls a material apart by trying to stretch is known as Tension force.
Tension creates an outward force, pulling the object/body away from each other.
It is represented by symbol ‘T’.
Materials that are ductile, such as Aluminium, Steel are used for resisting tensile forces.
Ropes, Nail, Thread are some examples where tensile force works.
Formula to derive Tension-
T= m*g
Where m= mass in kg, g= 9.8m/s^2
Tensile stress is referred to the tension force per unit area. Tensile strain is the ratio of increased length to the original length of the object.
A note on Compression:
Compression means ‘Being pressed’ . Forces that results in compaction or squeezing of an object acting towards each other is known as Compression Force.
As the relative positions of atoms and molecules of an objects changes due to compression force acting on it, it results in compaction.
This changes can either be temporary or permanent depending on the type of material.
Brittle materials like ceramics, concrete, glass are used to resist compressive forces.
The materials that can withstand compressive forces with little deformation are good for buildings as compression force is responsible for deformation of an object.
Compression Force is measured in ‘Newton’, represented by the symbol ‘C’.
Formula to derive Compression:
C= m*a
Where m= mass in kg, a= 9.8m/s^2
Compressive force per unit area is referred as Compressive Stresses, Compressive strain is the ratio of reduced length to the original length.
Purpose:
Compression helps in stabilizing various level of substrates such as gravel.
It provides strong and compacted base material.
Compaction is the compression of the material. It helps to remove air-gaps as much as possible.
Compaction also improves in packing of material.
Both tension and compression is experienced by a material undergoing bending.
When a load is applied on a beam, the upper part tends to bend experiencing compression by pushing it downwards, on the other hand the bottom part experiences a pull i.e. tension.
Reinforced cement concrete is used for beam casting as it experiences both tension and compression.
Example of dissipation is an arch bridge, whereas that of transfer is a suspension bridge.
Tension Vs Compression – Comparative Study
| Tension | Compression |
| Elongation of a material. | Shortening of a body/object. |
| Generally applicable to strings. | Applicable to any material. |
| The movement of force tends to be outside the object. | The movement of force is inward, towards the body. |
| Pulls material apart. | Squeezes material together. |
| Related to pulling on the end of an object. | Linked with pushing at the edges of an object towards centre. |
| Tensile forces are applied to materials that are ductile like steel. | Brittle materials like glass withstands Compressive Forces. |
Concrete Structures are divided into three categories on the basis of tension and compression-
- Compression Member
- Flexural Member
- Tension Member




