7 Types of Building Structures in Construction
The term structure refers to anything that is formed or made from interconnected elements and has a fixed location on the ground in the built environment. Buildings are included, but anybody constructed to take loads, even if it is not intended to be occupied by humans (engineers refer to them as ‘non-building’ structures – such as bridges, tunnels, and so on) can be included.
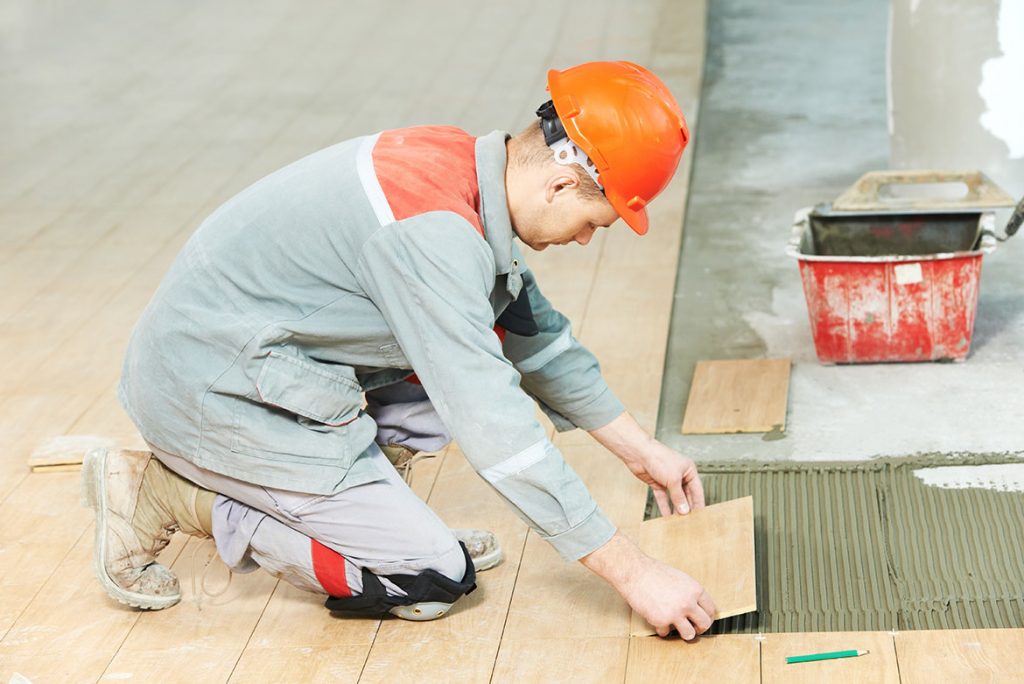
1. Load Bearing Structure:
The weight of a load-bearing structure is transferred to the walls in the form of roofs and floors supported directly on the walls in a load-bearing structure.
The load is transferred to the underlying soil via wall footing that is ideal and cost-effective for two to four-story buildings.
Because of its load-bearing purpose, the wall thickness decreases as the number of stories increases.
This structure is used when firm strata are accessible at shallow depths and the wall footings are placed directly on them.
Load-bearing structure benefits include:
- The load-bearing construction is extremely strong and long-lasting.
- These constructions are extremely fire resistant.
- Masonry units come in a variety of colors and textures, allowing for a lot of creativity.
- These structures don’t need to be prepared in advance.
- They have a pleasing appearance.
- Masonry construction tools and equipment are simple and inexpensive.

2. Pre-engineered Structure
The ideal building structure is sometimes pre-engineered because it goes together quickly and allows you to start utilizing it sooner than you expected. Often, you can design the building to your requirements, and then the sections are manufactured and assembled before being sent to the job site.
Pre-engineered products have the advantages of being quick to assemble, sturdy, and simple to personalise.
3. Truss Structure
A truss is a type of truss that is utilized in structures with a large span but little depth. A truss is made up of thin parts that are placed in a triangle pattern. A planning truss is a truss that has all of its members in the same plane and is commonly used for bridges. The space truss is made up of three-dimensional parts.
Loads that cause the truss to bend are converted into tension and compression forces by truss. Because of these advantages, truss uses fewer materials than beams and is made up of slender and long parts. Trusses can span distances ranging from 9 metres (30 feet) to 122 metres (400ft).
4. Cable and Arches
Cables are used to support long spans where truss is not feasible and could result in a significant increase in structure cost and size. Cables carry loads in tension and can be used for spans longer than 46m(150ft). Cables are also used in bridge structures, but their use is limited by their sag, weight, and anchorage method.
Arches commonly used in bridges and dome roofs transport loads in compressions, and the arch should be rigid to retain rigidity and forms. Secondary loading involves shear and moment, and these secondary loadings must be considered in the design.
5. Wood Frame Structure
Wooden frame buildings have been present for a long time, and they are the oldest of all building structures. It is also the type that is most widely used around the world. These constructions are entirely constructed of wood that is cut and assembled on-site. That means the workers are cutting the studs, plates, joists, and rafters as needed and installing them before the drywall, paneling, and other materials are installed.
The advantages of timber frame building structures include the fact that the materials are renewable, the cost is relatively inexpensive, and they can be constructed fast using common construction tools. Of course, there are drawbacks, such as the building being combustible, prone to deterioration owing to the environment, and insufficiently sturdy to withstand hurricane and tornado gusts.
6. Tension Structures / Tensile Structures
A tensile structure is made up of exclusively tension-carrying parts with neither compression or bending. Tensile membrane structures are commonly utilised as roofs because they can span great distances inexpensively and beautifully. Sports facilities, warehousing and storage facilities, and exposition venues are all examples of this type of structure. The types, shapes, and benefits of tensile constructions are briefly discussed in this article.
Advantages of Tensile Structures
- Environment protection (sun, rain, wind)
- Translucency in general, as well as the ability to create light effects
- Durability and little weight
- Form options are endless, and the character is captivating.
- Short construction duration, structural manufacture off-site, and less time on-site disruption
- Large stretches of time
- Eco-friendliness and recyclability
- Adaptability to cutting-edge construction technology (steel, glass, cement, stone)
- Maintenance is simple, and repairs or replacements are simple.
7. Composite Structures
The non-residential multi-story building industry is dominated by composite construction. For more than two decades, this has been the situation. Its success can be attributed to the strength and stiffness that can be achieved with the least amount of materials.
Concrete is good in compression, while steel is good in tension, which is why composite construction is typically so good. These qualities can be leveraged by structurally connecting the two materials together, resulting in a highly efficient and lightweight construction.