13 Components of Building Structure | Building Structure Basic Components
13 Components of a Building Construction Structure
Any structure built to satisfy the needs and purposes of users is referred to as a building. Residential, commercial, institutional, educational, assembly, industrial, storage, and other sorts of buildings are designed by an architect or structural designer and built by a civil engineer.
A structure is made up of numerous components. A Civil Engineer should be well-versed in the execution of each and every component in accordance with the architect’s design layouts.
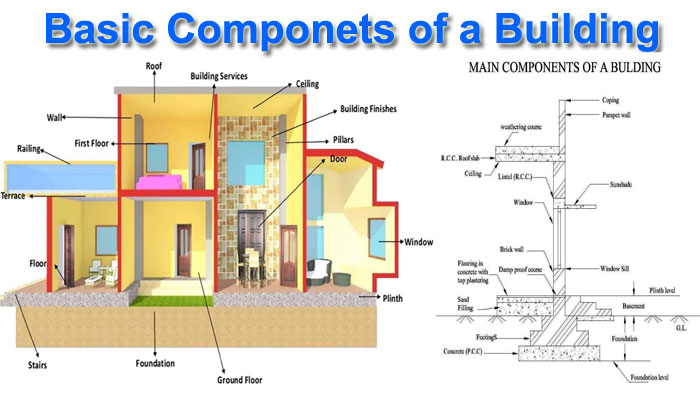
1. Foundation
A building’s foundation is its foundation. As a result, it serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the structure is built. To avoid settlement damage, the building loads should be evenly distributed over the base in response to the soil depth. For the best foundation, a firm foundation is preferred.
2. Beam
Beams are the building’s horizontal elements. The load from the slab is carried into the columns by the beams in the case of construction. The beam is made of reinforced cement concrete (R.C.C.). In general, there are various types of beams that are commonly used in building projects and are classed according to the following criteria.
3. Plinth Beam
A plinth beam is a type of beam structure that provides settlement stability and acts as an earthquake defender. Between the ground and the floor, a plinth beam is usually found. By raising the floor above the ground level, it helps to prevent surface water from entering the building.
4. Tie Beam
The tie beam is the beam that extends above the plinth level. They serve as a length breaker in the columns and serve as a frame for the construction.
- Based on Support Conditions
- Based on Construction Materials
- Based on Cross-Section Shapes
- Based on Geometry
- Based on Equilibrium Condition
- Based on Construction Method
- Based on Support Conditions
5. Column
Above the ground level, columns are built. Architectural columns and structural columns are the two types of columns. Structural columns are designed to support the weight of the slabs above them and transfer it to the foundation. Architectural columns, on the other hand, are constructed solely to meet a building’s aesthetic requirements.
6. Floor
The plane above the plinth level is the floor. Tiles, granites, marbles, concrete, and other materials are utilized for flooring. Before installing flooring, the ground must be adequately compacted and leveled. The ground floor, first floor (above the ground floor), second floor (above the first floor), and so on are examples of different levels of the floor.
7. Stair
A stair is a set of stairs that are designed in a specific order to connect different floors of a building. A stairway is a space that a stair occupies. A staircase refers to the apartment or room in a building where a stair is located. The most popular forms of staircases include wooden stairs, R.C.C stairs, brick stairs, metal stairs, and so on.
8. Wall
A building’s vertical part or component is the wall. There are two sorts of walls: load-bearing and non-load-bearing. It can be made from mud, stones, bricks, concrete blocks, and other materials. Insiders are protected from elements such as rain, wind, sunlight, wild animals, and societal foes by walls, which also provide seclusion.
9. Opening
Different openings in a building are formed by doors, windows, and ventilators. Doors are used to enter the chamber, while windows and small ventilators are installed in the walls to offer light and ventilation.
10. Lintel
Just above the holes, a stone slab or a concrete slab known as LINTEL is built to support the walls above the openings. SILL, on the other hand, is constructed just below the window.
11. Roof
The roof is the most visible part of building construction, and it protects the structure from the elements. It primarily covers the walls and columns. Roofs are made of thatch, leaves, stones, clay, bricks, tiles, R.C.C., and other materials. Roofs exist in a variety of shapes, but they become flat in low rainfall areas and sloppy in high rainfall or snowy areas, depending on the environmental variables.
12. Parapet
In the case of flat roofs, the parapet is essentially a short safety wall that extends over the roof slab.
Read more about Parapet Wall Types
13. Coping
A coping is a structure that is built over a boundary wall or parapet to shelter brick masonry walls from direct sunlight and rain. Furthermore, it is employed to improve the building’s aesthetic appeal.